What is Learning according to Social Learning Theory?
Social Learning is represented by the construction of specific behavioral patterns that are acceptable in a particular social group. Therefore learning is acquired by observing others’ behavioral patterns and the outcomes of those behaviors.
Page Content
Infographic 1
Infographic 2
Learning Situation
Observation Checklist
Reflection
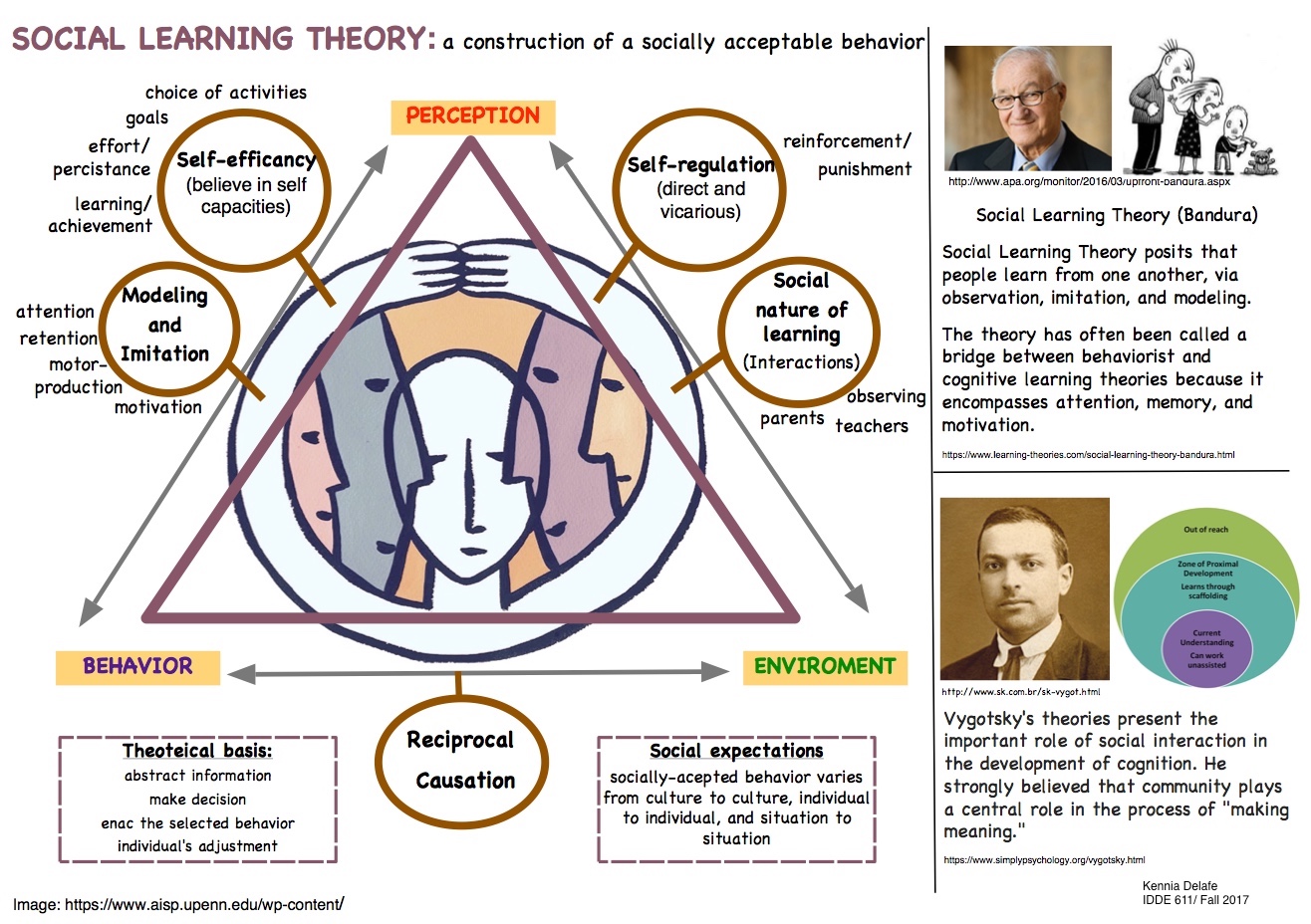
Infografic 1
Click on the following link to access to the pdf life: SocialLearning-Infographic.pdf
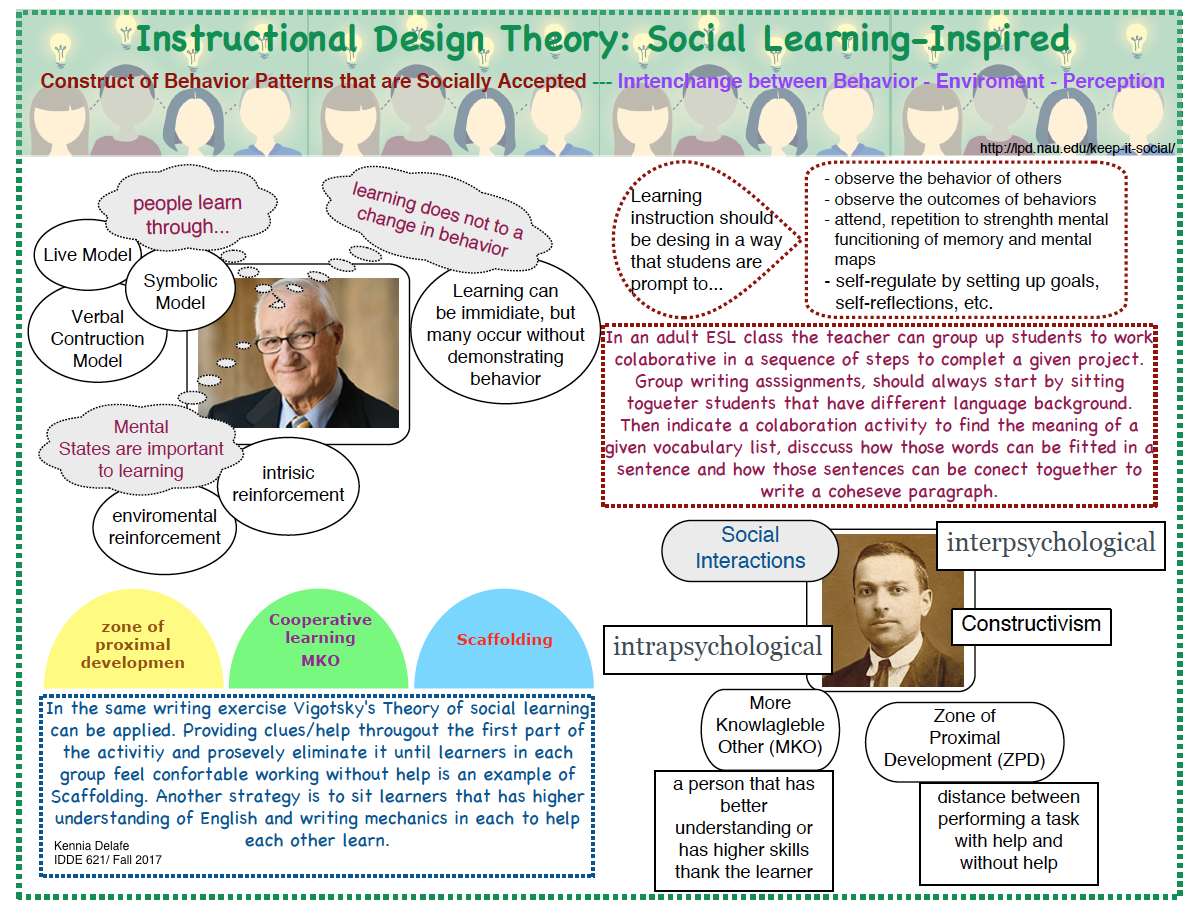
Infographic 2
Click on the following link to access to the pdf file: Instruction-based-Social LearningTheory.pdf
Examples of Instructional Design Theory in practice:
Discovering social learning from within the learning scenery, Blog by Kaja Jurtela and Matija Čarman. Information retrieved from http://knowledgehub.cef-see.org/?p=555

How to integrate Social Learning into the Classroom, Article by Amy Happ, Advantexe Learning Solutions
retrieved from: https://trainingindustry.com/articles/workforce-development/how-to-incorporate-social-learning-into-the-classroom/
Learning Situation
Title: Basic English Grammar for Adult ESL Students
The teacher writes two sentences on the whiteboard: “I am a teacher.” and “You are students.” She reads them at loud, then asks the students to repeat them after her. She points at the words as she reads and the students follow her reading at loud. “Great!” She says. She asks students to read them one more time, but she only points at the words while the students read the sentences. The teacher smiles pleased. Today, we are going to learn the basic structure of a sentence, the teacher says.
The teacher points at the first word of the first sentence and explains “this is the Subject of the sentence. In the subject you can write Pronouns like I, you, she, he, it, we, they. Then she points at the second sentence and asks students what the subject is. Students look at it and respond ‘I’ at loud. The teacher says That’s the correct answer!
Then the teacher points at the verb To Be in the first sentence and explains that it refers to places and descriptions and that it changes into three-forms (am, is or are) depending on the subject. Then she explains that (am) is used for the subject I, (is) is used for the subjects she, he, and it, and (are) is used for you, we, and they.
She points at the second sentence and asks students which of those words is the verb Be. The students answer, ‘are’ and then the teacher says “Excellent! You are good students.” The teacher points to the last word and explains that “Teacher” is a noun and that nouns name all people, animals, places, and things. The teacher asks students to name some people, animals, places, and things they know. Students randomly answer while she writes some of them on the board. Then she points at the second sentence and asks which is the noun in that sentence. They shout “students!” and very excitingly the teacher says “Awesome! You are my best students!”
To assess students knowledge, the teacher hands out outlined papers and asks them to write 3 to 5 sentences using the Subject + BE + noun structure. Students ask the teacher for review as they complete the assignment. Teacher checks, and asks students to re-write the sentences after explaining and correcting mistakes. Once tasks are completed, the teacher asks students to stand up one at the time to write one of their sentences on the boar, and report back to the class pointing at the subject, verb, and noun. The teacher steps back and lets peers correct mistakes as students write and report to class their completed sentences. Classmates cheer others as they see the sentences completed correctly.
Click on the following link to access to the pdf file: CaseStudy-Social Learning.pdf

Learning Situation Observations:
- During this part of an ESL for adults lesson, the teacher explicitly models the behavior she wants the students to construct by the end of the experience while she prompts their attention by asking questions throughout her explanations.
- She expresses clear lesson’s goals after she models acceptable grammar structure in the English language while interacting with students.
- The teacher practices scaffolding techniques throughout the lesson by helping and modeling the grammar structure to students until they can continue on their own.
- There is an opportunity for students to observe others’ behaviors and the result of it when students are participating while they elicit positive or negative verbal reinforcers from the teacher.
- Students socially interact with others as part of their practice and have the opportunity to self-observe, self-judge, and self-react their performance while coopering and learning from each other.
- The environment supports students learning experience by having all the materials needed accessible (grammar structure, vocabulary, teacher’s help…) and the opportunity of interaction with everybody for a reciprocal teaching.
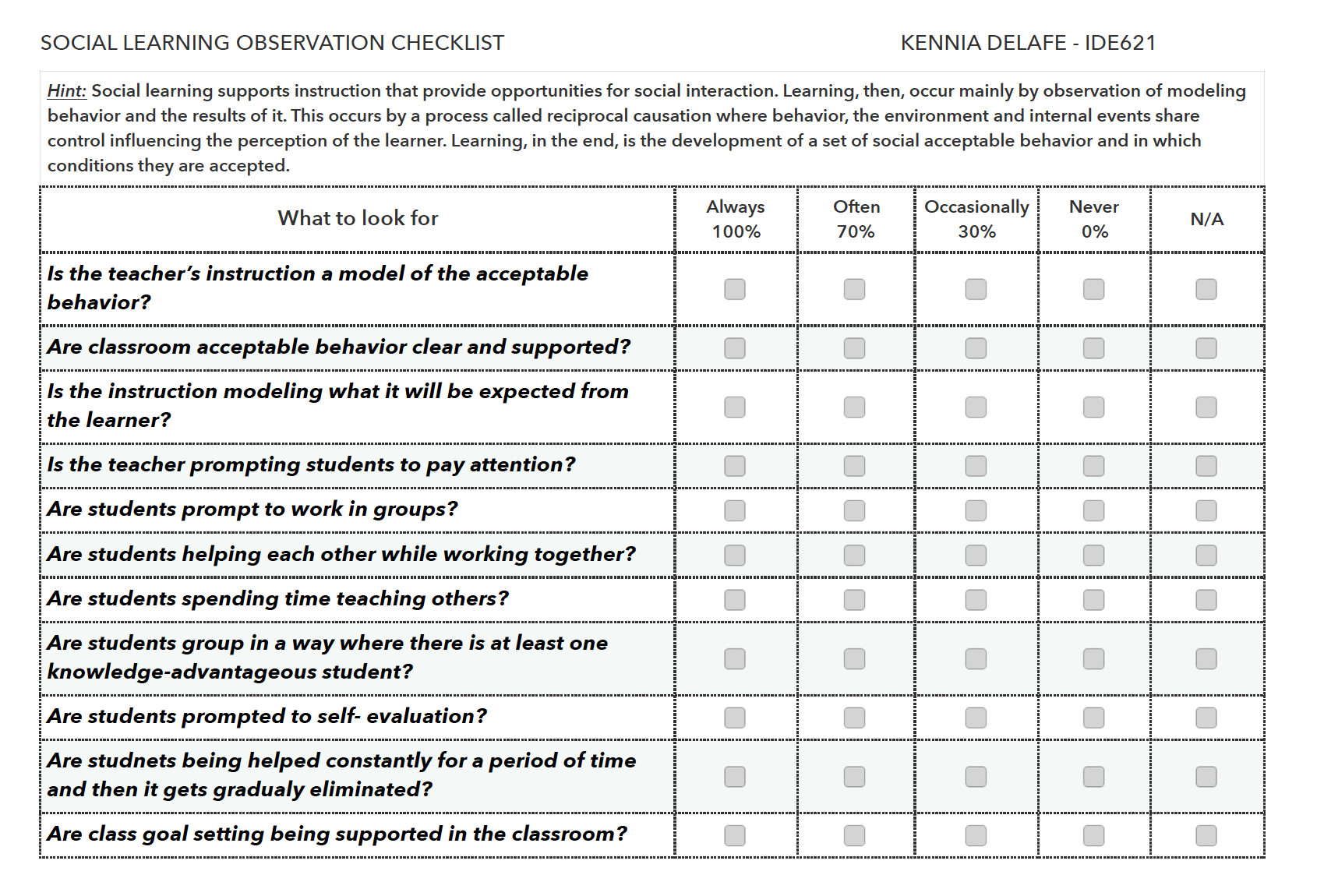
Observation Checklist
Click on the following link to access to the pdf file: SocialLearningObservation Checklist.pdf
Reflection
Social Learning Theory was the last one we study in this training and with which I felt very connected. It says that we learn by interacting with the environment and by observing how others behave and the result of those behaviors and this is exactly me. To learn, I need to communicate with the content, with the instructors, and with everybody else. No one believes me when I say that I am an introvert person because I am always on the “go.” For me, learning is so vital that interaction becomes a reflection of my needs, not my personality type.
Observing how others do things, thinking about how it reflects what I am learning and trying it afterward I believe is essential. Being able to collaborate with others, have reciprocal teaching, serve as a live-model, compare what I know about with what I am learning and experience information from a different point of view is very important as well. One of the experiments we did in this class that helped me to reaffirm what I am writing here now is the VARK inventory we took before the first day of course. The results of it state that I am a visual and Kinesthetic learner.
In my daily ESL instructions, I always put into practice social learning theory. I model and prompt attention from my students to better learn what the acceptable behavior for the lesson in practice is. I teach them how to set up realistic goals for and how to reach them according to their English knowledge level. I like to give them time to experience the given concepts by themselves and with others practicing with partners or completing exercises in groups. I promote discussions, pair-instruction, and pair-review. I set up time for them to ask questions and connect new information with old ones. I teach them how to learn to learn by experiencing the same exercise from different angles and discussing their findings. In the way, I use reinforcements that “shape” the acceptable approach in the various classroom situation. We enjoy learning to form each other.
Therefore, I believe that for me the best learning approach is by using the social learning theory.